Learn More About Milestone Solutions
Call us at +1-408-200-2211 or fill the form below
*Required Files
Your privacy and security are a top priority. We will not distribute or sell your personal information to any third parties. Please visit our privacy policy page to contact us to review or delete data collected.
Maximize Search Visibility with Advanced Schema Markup
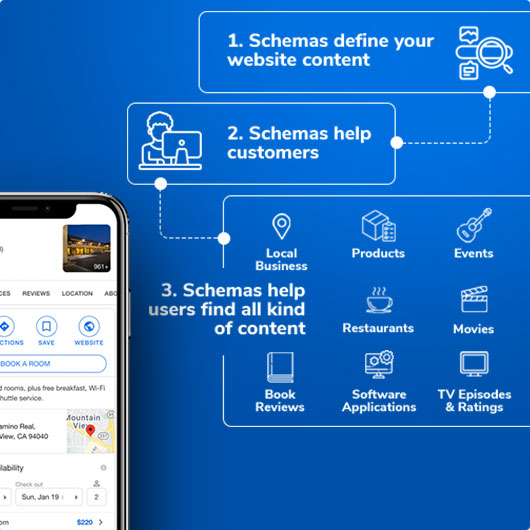
Schema markup, or structured data tagging, helps search engines and LLM-based AI tools understand your content better and surface it in answers to relevant queries. It also helps you maximize the visibility of your content in rich results and other search features.
Search algorithms are increasingly powered by artificial intelligence (AI) for understanding entities within the content of websites. AI tools such as ChatGPT, Google's Gemini, Microsoft's Copilot, Perplexity and others are completely powered by AI. The understanding of entities is very much a part of LLM answers. This makes advanced schemas the SEO/GEO initiative with the highest ROI and the fastest growth.
Schemas are detailed metadata that help search engines and LLMs read and understand the context of your content and related facts, yet only 40% of websites use schemas at all, and fewer than 10% use advanced schema markup. While schemas are essential for your universal search presence and indexing, adding them manually is time-consuming, error-prone, and costly.
As more consumers use Generative AI experiences, marking up and interconnecting entities in your content with schemas will help your content be more visible.

Top Schema Manager Benefits
How To Succeed with Schema Management
For schema markup to be effective, here are the 8 things you need:
- Advanced schema architecture that uses all schema types relevant to your business and the type of content on the page.
- Nesting of schema types to maximize interconnection and relationships between the various content elements or entities.
- Deployment at scale to mark up large websites.
- Constant monitoring of errors and warnings to ensure error-free schemas on your site.
- Quick turnaround to fix schema errors.
- Continuous monitoring of changes in schema vocabulary or definitions to keep tagging up to date.
- Content that covers all mandatory and optional attributes that can be marked up or tagged with schemas.
- Performance reporting to demonstrate results, ROI, and business value.
With Milestone Schema Manager, you get all the above and more. Our no-code schema solution helps you deploy schema markup at scale with virtually no engineering or web development resources.
Schema management that drives results
Milestone Schema Manager makes creating and maintaining error-free schema markups for your website easy. Create relevant schemas for your business, products, services, and locations, and then publish them to your site by adding just one line of code to your tag manager or head section. We do the hard work, so you don't have to.
- Increased impressions and traffic from rich snippets, and People Also Ask with performance gains of 20% to 80%
- Easy discovery and identification
- Complete reporting on schema tagging and performance
- Error elimination & warning fixes, and schema.org updates
- Efficiency of schema creation and 1 milisecond injected deployment
- Scalability: Milestone Schema Manager enables you to optimize one million pages
- Advanced performance and ROI reporting
Top Milestone Schema Manager Benefits
- Automation at scale: Milestone Schema Manager auto-discovers the schema code on your website.
- Schema recommendations: The recommendation engine suggests relevant schema types based on your content and automates schema tagging and deployment at scale. It makes adding schema markup easy while reducing resources and costs.
- Error-free Schemas: The built-in validation engine automates schema validation to ensure error-free schemas.
- Instant Indexing: Milestone's partnership with IndexNow automatically informs search tools when you make updates to your website and gets your content indexed and findable faster.
- Designed for testing: You can test the impact on a section of your site, a category or a page type and compare the results against a test group to demonstrate ROI and growth.
- Constant monitoring: Identify schema errors early and deploy fixes instantly to reduce the impact of schema errors.
- Schema Drift: This feature detects changes in text content on the page and automatically updates the associated Schema tags with that information.
- Platform independent: Milestone Schema Manager is a SaaS solution that works with all CMS platforms and all tag managers.
- Core Web Vitals Friendly: Milestone Schema Manager does not impact the speed and performance of your website.
- No developer experience required: All you need to do is add one line of code to your tag manager (works with Google Tag Manager, Adobe Tag Manager and others). We do the rest. We even have a plugin made for Adobe Experience Manager.
- Performance reporting: Advanced performance reporting is built into the platform to help you monitor and report on performance, measure ROI and demonstrate business value.
Grow your business with Schema Manager
- Milestone Schema Manager requires your development team to add just one line of code to your tag manager. That is all the engineering you will have to do.
- Once deployed, Milestone Schema Manager identifies relevant schemas that your content can be marked up with.
- It auto-generates the code that wraps schemas around your content and tags the relevant entities within your content.
- It helps you inform search engines what your business is, the products you offer, hours, FAQs, images, videos, and other key information that boost your digital presence and position in search results.
- The Milestone advanced schema solution has been deployed on over 10,000 SMB and global enterprise websites and has consistently delivered 25-60% increases in organic impressions on search engines and traffic across installations, making it the most ROI-positive digital marketing strategy your business can adopt.
Schema deployment made easy in our digital platform
- Typically, schema deployment on a website requires both IT and marketing resources on an ongoing basis.
- Milestone's Schema Manager enables frictionless schema deployment and maintenance with very little work required from website IT resources.
- Milestone Schema Manager helps enhance your technical SEO strategy and efforts.
- Ongoing automated crawls and monitoring help you detect and fix schema errors quickly
- Google Search Console and analytics integration help you monitor the impact
- With advanced reporting capabilities, you can measure the impact and demonstrate the ROI and cost savings
The importance of automated schema deployment and management services
While schemas are essential for your universal search presence and indexing, adding them manually is time-consuming, error-prone, and costly.
• Our managed schema management services help with both schema deployment and maintenance.
• We help you identify and deploy the right schema types in an advanced nested architecture.
• We validate the schema code to ensure error-free schema deployment.
• We constantly crawl and monitor the site to identify and fix schema errors that may arise as a result of changes in your content or schema vocabulary.
• We constantly update our schema library with new schema types as they become available. You are always assured of the latest schema types.
• We periodically check in with your team to update you on the status of your project, the results achieved, and more.
• Our schema return on investment (ROI) calculator measures the expected profit you will earn from your content marketing, SEO, or local business marketing investment in error-free advanced schemas.
Test the health of your website schema for free!
-
What is Schema Markup?
-
Why should I have schemas on my website?
-
How does schema markup help with SEO and GEO?
-
What are the different types of schema markup?
-
What is the recommended format for implementing schema markup?
-
How does schema markup work?
-
What are the challenges with schema markup implementation?
-
Does schema markup help get seen in rich snippets?